√ p(x 2) probability calculator 797561-How to get p(x) in statistics
The cumulative density function (CDF) aka the cumulative distribution function;Calculator to find out the standard score, also known as the zscore, of a normal distribution, convert between zscore and probability, and find the probability between 2 zscores Also explore many more calculators covering probability, statistics and other topicsHow to calculate discrete uniform distribution?
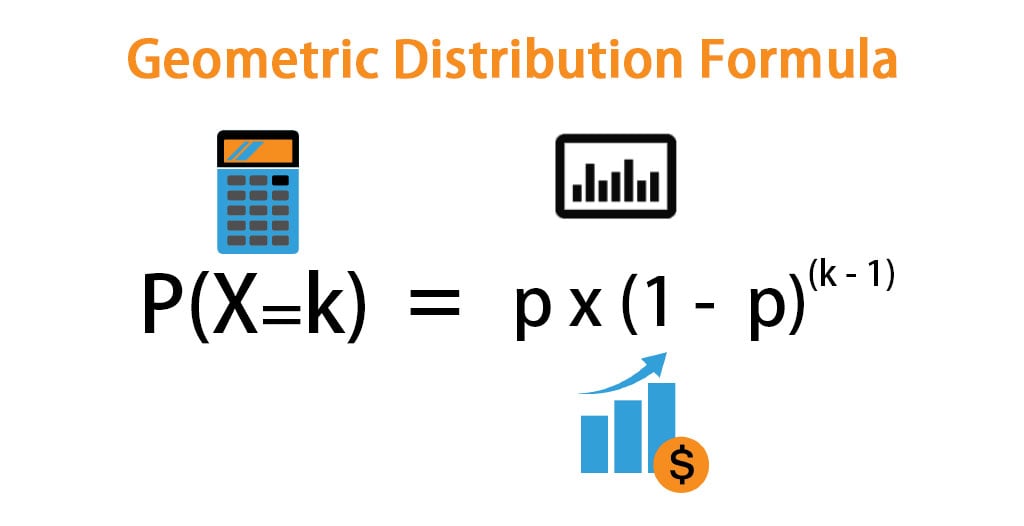
Geometric Distribution Formula Calculator With Excel Template
How to get p(x) in statistics
How to get p(x) in statistics-Cumulative Binomial Probability Calculator This calculator will compute cumulative probabilities for a binomial outcome, given the number of successes, the number of trials, and the probability of a successful outcome occurring For the number of successes x, the calculator will return P(Xx), and P(X≥x)The Single Event Probability Calculator uses the following formulas P(E) = n(E) / n(T) = (number of outcomes in the event) / (total number of possible outcomes) P(E') = P(not E) = 1 P(E) Where P(E) is the probability that the event will occur, P(E') is the probability that the event will not occur, n(E) is the number of outcomes in the event E,
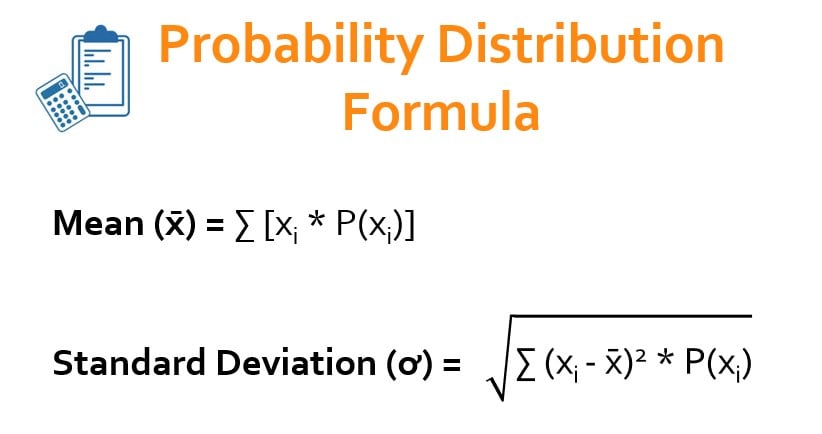


Probability Distribution Formula Examples With Excel Template
P(x) is the probability of x successes occur in the n number of events, p is the probability of success and q is the probability of failure often denoted by q = (1 p) The binomial distribution arise for the following 4 conditions, when the event has 1 n identical trials or experiments 2Maybe the quickest way to do this is to find the probability that they're both less than 2, and then subtract that from 1 Pr (X < 2 & Y < 2) = Pr (X < 2) Pr (Y < 2) = 2 4 ⋅ 2 3 = 1 3 Therefore the probability that at least one of them is more than 2 is 2 / 3Negative Binomial Distribution Calculator This calculator is used to find the probability and cumulative probabilities for negative binomial random variable given the number of successes Read moreNegative Binomial Distribution Calculator with Examples
Given random variables,, , that are defined on a probability space, the joint probability distribution for ,, is a probability distribution that gives the probability that each of ,, falls in any particular range or discrete set of values specified for that variable In the case of only two random variables, this is called a bivariate distribution, but the concept generalizes to anyConditional Probability is a mathematical function or method used in the context of probability & statistics, often denoted by P(AB) to represent the possibility of event B to occur, given that the even of A already occurred, and is generally measured by the ratio of favorable events to the total number of events possible The probability of conditional event always lies between 0 and 1 andProbability Calculator is an online tool to calculate the chance Our simple Probability calculator for multiple events, single event and two events Calculatorstech Calculator Type {Probability of } X = 0 is 025 Probability of X = 0 i s 0 2 5 Probability of X = 1 i s 05 \text
(e) Find the probability that he correctly answers fewer than 2 questions This is asking for \(P(X 2)\) Since this is counting down, we can use binomcdf But, the event "fewer than 2" does not include 2 So, we will put 1 into the cdf function \(\begin{align} P(X 2) &= \text{binomcdf(12, 025, 1)}\\ &\approx \boxed{}\end{align}\)Poisson distribution calculator calculates the probability of given number of events that occurred in a fixed interval of time with respect to the known average rate of events occurred It's an online statistics and probability tool requires an average rate of success and Poisson random variable to find values of Poisson and cumulative Poisson distributionCalculate the probability of getting 5 heads using a Binomial distribution formula P(x=5) = ;
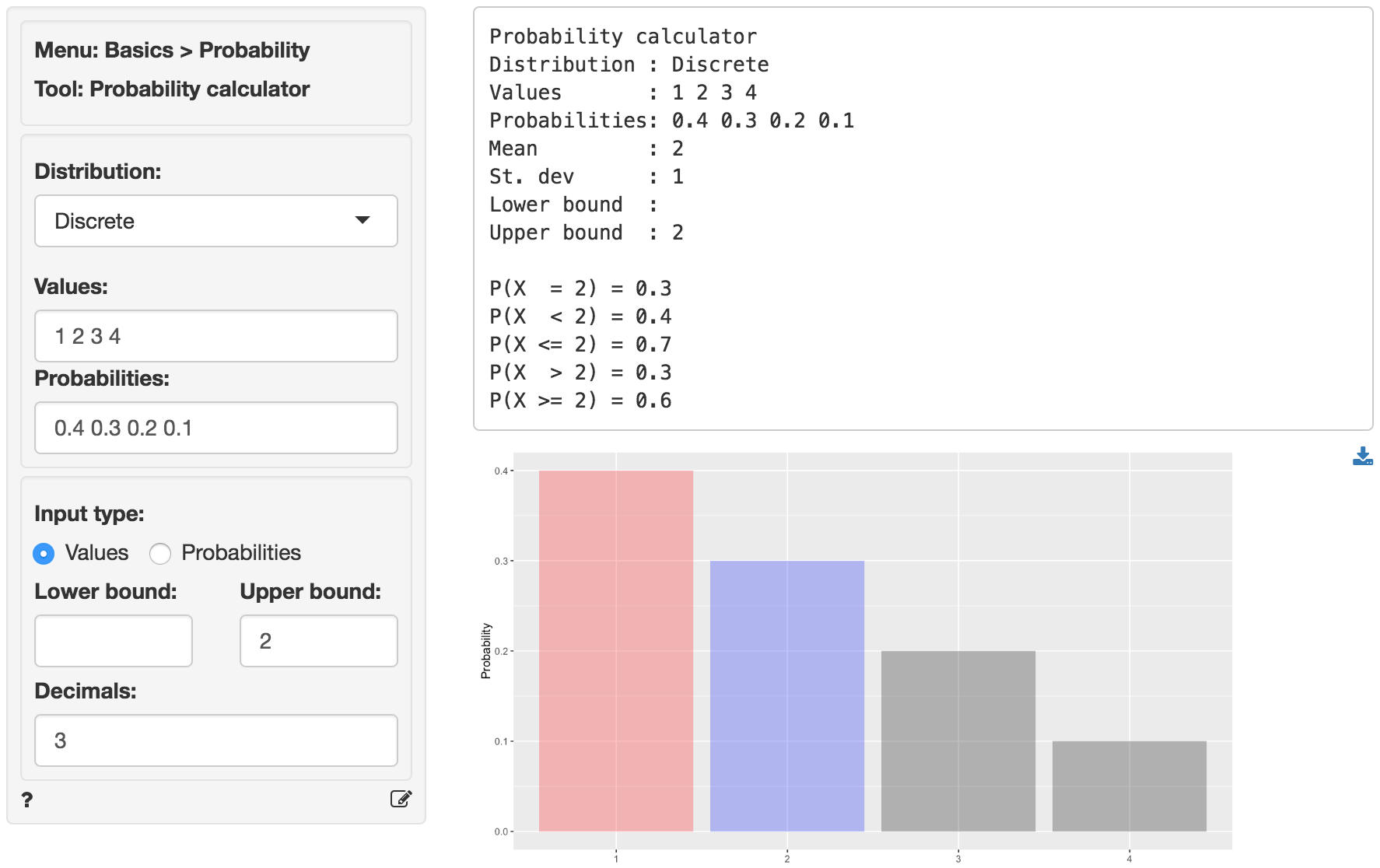


Basics Probability Probability Calculator
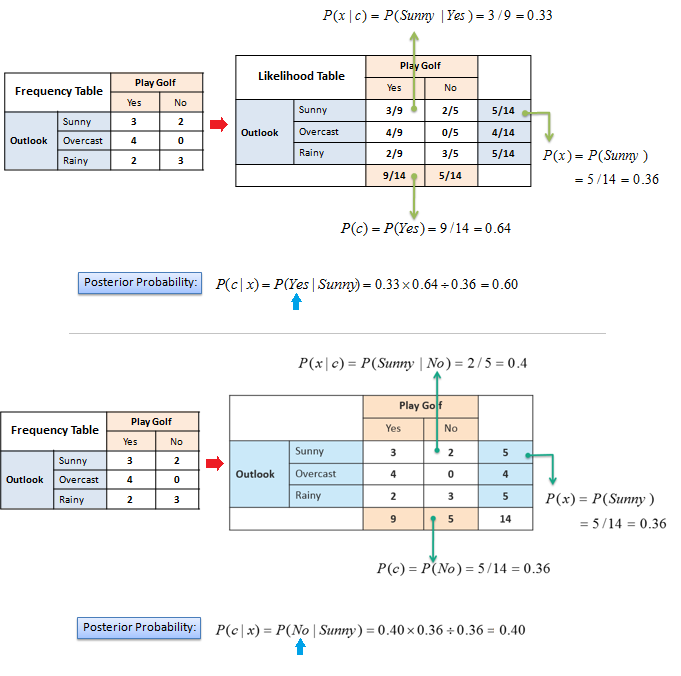


Naive Bayesian
(e) Find the probability that he correctly answers fewer than 2 questions This is asking for \(P(X 2)\) Since this is counting down, we can use binomcdf But, the event "fewer than 2" does not include 2 So, we will put 1 into the cdf function \(\begin{align} P(X 2) &= \text{binomcdf(12, 025, 1)}\\ &\approx \boxed{}\end{align}\)The probability of getting exactly 5 successes is Binomial Distribution Formula – Example #2 In a study, it is found that 70% of people who purchase pet insurance are mostly women If we randomly select 9 pet insurance ownersEach of these is defined, further down, but the idea is to integrate the probability density function \(f(x)\) to define a new function \(F(x)\), known as the cumulative density function



Geometric Distribution Formula Calculator With Excel Template



Probability Calculator Statistical Software For Excel
Maybe the quickest way to do this is to find the probability that they're both less than $2,$ and then subtract that from $1$ $$ \Pr(X3) CP for P(x > x given) is equal to 1 P(x ≤ x given) 4) CP for P(x ≥ x given) is P(x = x given) P(x > x given) Where CP = Cumulative Probability Example of a calculation Let's consider that in average within a year there are 10 days with extreme weather problems in United States So what is the probability that United StatesThe probability of rolling at least X same values (equal to y) out of the set the problem is very similar to the prior one, but this time the outcome is the sum of the probabilities for X=2,3,4,5,6,7 Moving to the numbers, we have P = P(X=2) P(X=3) P(X=4) P(X=5) P(X=6) P(X=7) = = % As you may expect, the result is a
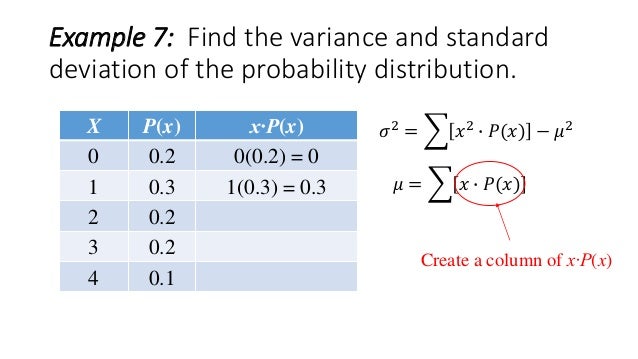


Variance And Standard Deviation Of A Discrete Random Variable
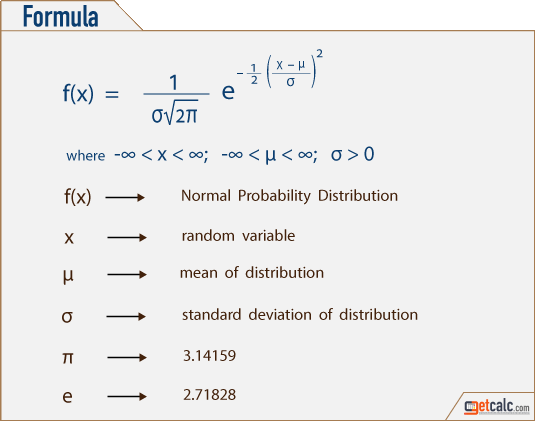


Normal Distribution Calculator Formula Examples
Uniform distribution probability (PDF) calculator, formulas & example work with steps to estimate the probability of maximim data distribution between the points a & b in statistical experiments By using this calculator, users may find the probability P (x), expected mean (μ), median and variance (σ 2) of uniform distribution3) CP for P(x > x given) is equal to 1 P(x ≤ x given) 4) CP for P(x ≥ x given) is P(x = x given) P(x > x given) Where CP = Cumulative Probability Example of a calculation Let's consider that in average within a year there are 10 days with extreme weather problems in United States So what is the probability that United StatesEnter the mean and standard deviation for the distribution Enter the chosen values of x 1 and, if required, x 2 then press Calculate to calculate the probability that a value chosen at random from the distribution is greater than or less than x 1 or x 2, or lies between x 1 and x 2



4 Ways To Calculate Probability Wikihow
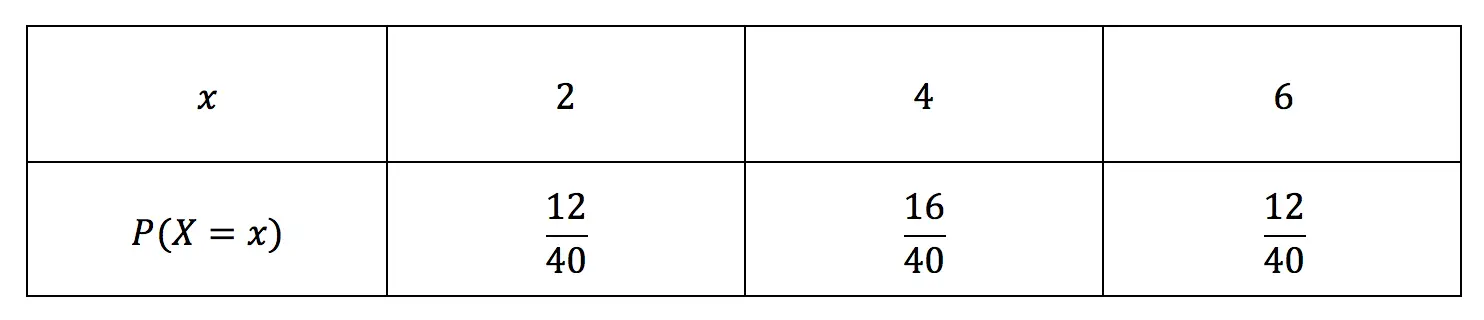


Parameters Of Discrete Random Variables
Choose 𝑥 1 to calculate the cumulative probability based on the percentile, or p(X≤𝑥 1) to calculate the percentile based on the cumulative probability 𝑥 1, 𝑥 2 to calculate p(𝑥 1 ≤X≤𝑥 2) Probability density function (PDF) For a continuous distribution the density is the derivative of the cumulative distribution functionGiven a probability of Reese's being chosen as P(A) = 065, or Snickers being chosen with P(B) = 0349, and a P(unlikely) = 0001 that a child exercises restraint while considering the detriments of a potential future cavity, calculate the probability that Snickers or Reese's is chosen, but not bothHow to use Probability Calculator?



6 2 Using The Normal Distribution Texas Gateway


Www Stat Auckland Ac Nz Fewster 210 Notes 16s2 Ch4annotated Pdf
Finding To calculate the probablity P(X x) by hand, we would have to calculate each individual probability, P(0), P(1), P(2), , P(x), and then add those together The TI/84 calculator has a built in function that does this calculation in one step The function is binomcdf (n, p, x) To calculate P(X 3) given n = 4, p = 041, and q = 059, press 2nd VARS DISTR, ARROW DOWN to select ANormal Distribution Calculator Use this calculator to easily calculate the pvalue corresponding to the area under a normal curve below or a above a given raw score or Z score, or the area between or outside two standard scores With mean zero and standard deviation of one it functions as a standard normal distribution calculator (aka z table calculator), but you can enter any mean andThe probability of rolling at least X same values (equal to y) out of the set the problem is very similar to the prior one, but this time the outcome is the sum of the probabilities for X=2,3,4,5,6,7 Moving to the numbers, we have P = P(X=2) P(X=3) P(X=4) P(X=5) P(X=6) P(X=7) = = % As you may expect, the result is a
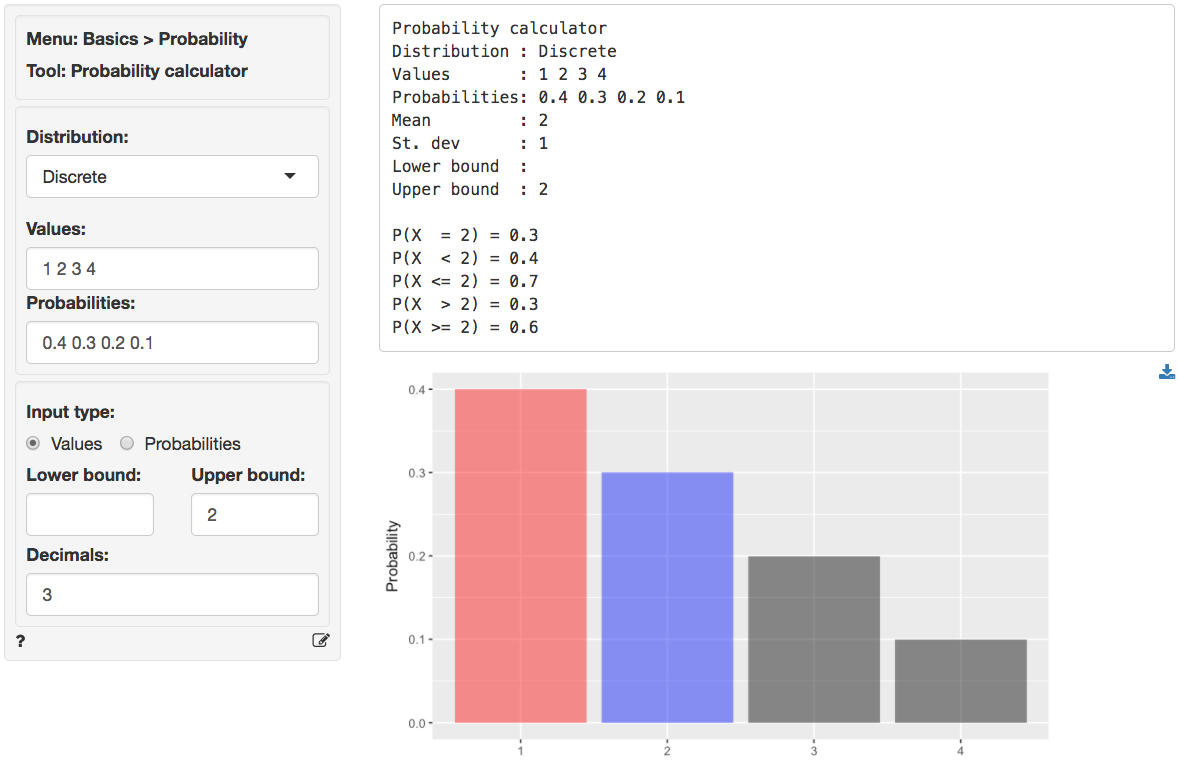


Basics Probability Probability Calculator
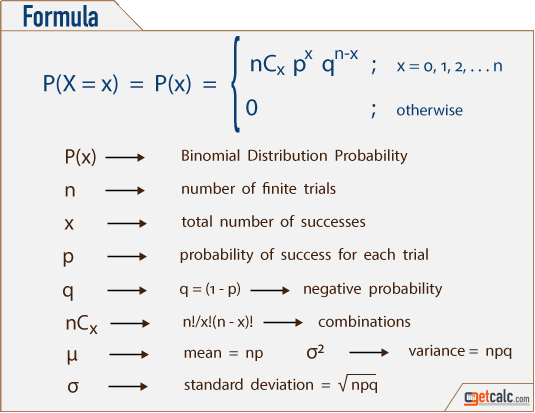


Binomial Distribution Formulas Calculator
Arithmetic Mean Geometric Mean Quadratic Mean Median Mode Order Minimum Maximum Probability MidRange Range Standard Deviation Variance Lower Quartile \frac{x^24x45}{x^2x30} simplify\\frac{x^214x49}{49x^2} Middle School Math Solutions – Equation Calculator Welcome to our new "Getting Started" math solutions series Over theStep 1 Enter the minumum value (a) Step 2 Enter the maximum value (b) Step 3 Enter the value of xThe Poisson Probability Calculator can find the probability of an event occurring given the average number of times the event occurs in a time interval = 34 $ and $ x = 5 $ into a poisson probability distribution function (PDF) If doing this by hand, apply the poisson probability formula $$ P(x) = \frac{{e^{\lambda}} \cdot {\lambda^x



Binompdf And Binomcdf Functions Video Khan Academy


Random Variables
X & ~0~ & ~2~ & ~5~ & ~7/3~ & ~5 \\ P(X) & ~01~ & ~02~ & ~1/3~ & ~1/6~ & ~02 \end{array} $$ Find the mean of the distribution example 4 ex 4 When you roll a die, you will be paid \$3 for numbers divisible by 3 and you will lose \$2 for numbers that are not divisible by 3 Find the expected value ofEnter the mean and standard deviation for the distribution Enter the chosen values of x 1 and, if required, x 2 then press Calculate to calculate the probability that a value chosen at random from the distribution is greater than or less than x 1 or x 2, or lies between x 1 and x 2Probability calculator is free and easy to use You just need to follow below steps Step #1 Define the probabilities of single or multiple events you want to calculate Probabilities must have two separate events Probability of A P(A) and Probability of B P(B) Step #2 Find the Probability of an event


Probability Calculator


2
Determine the probability that a randomly selected xvalue is between $15$ and $22$ example 2 ex 2 The final exam scores in a statistics class were normally distributed with a mean of $58$ and a standard deviation of $4$Instructions This Normal Probability Calculator for Sampling Distributions will compute normal distribution probabilities for sample means \(\bar X \), using the form below Please type the population mean (\(\mu\)), population standard deviation (\(\sigma\)), and sample size (\(n\)), and provide details about the event you want to compute the probability for (for the standard normalCalculating Probabilities To calculate probabilities we'll need two functions The probability density function (PDF);
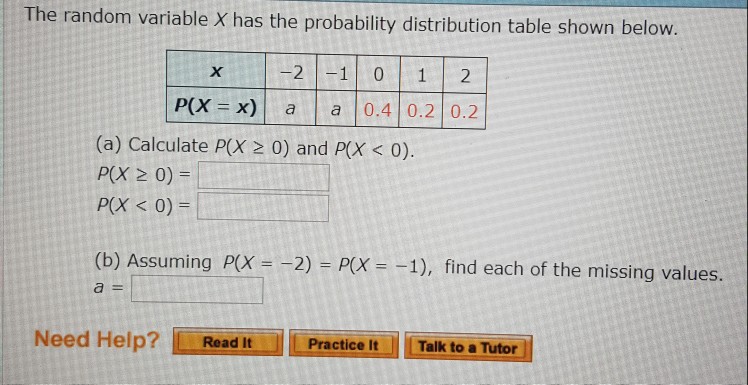


Solved The Random Variable X Has The Probability Distribu Chegg Com
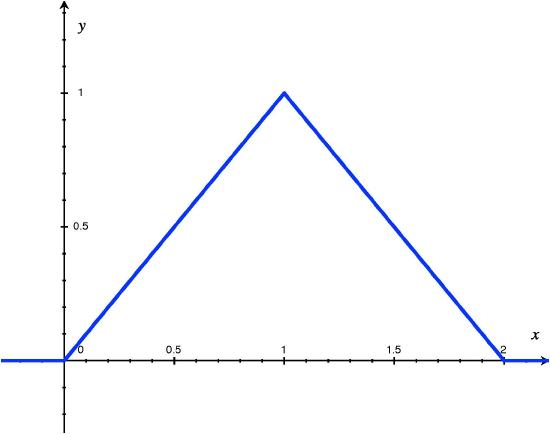


4 1 Probability Density Functions Pdfs And Cumulative Distribution Functions Cdfs For Continuous Random Variables Statistics Libretexts
Binomial Probability Calculator Use the Binomial Calculator to compute individual and cumulative binomial probabilities For help in using the calculator, read the FrequentlyAsked Questions or review the Sample Problems To learn more about the binomial distribution, go to Stat Trek's tutorial on the binomial distributionUniform distribution probability (PDF) calculator, formulas & example work with steps to estimate the probability of maximim data distribution between the points a & b in statistical experiments By using this calculator, users may find the probability P (x), expected mean (μ), median and variance (σ 2) of uniform distributionThis applet computes probabilities for the binomial distribution $$X \sim Bin(n, p)$$ Directions Enter the number of trials in the $n$ box Enter the probability of
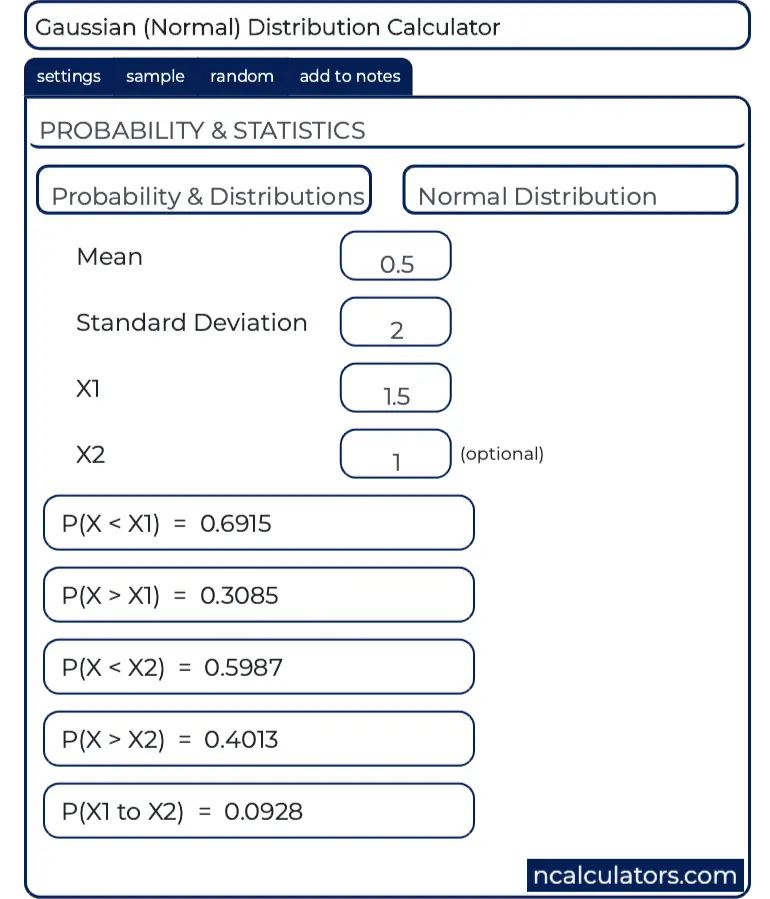


Normal Distribution Calculator


Probability Density Function
The probability distribution is described by the cumulative distribution function F(x), which is the probability of random variable X to get value smaller than or equal to x F(x) = P(X ≤ x) Continuous distribution The cumulative distribution function F(x) is calculated by integration of the probability density function f(u) of continuous(a) The probability of getting exactly 4 heads out of the six is PX = 4 = f(4) = , the height of the bar at x=4 in the probability distribution graph (the left one) (b) The probability of getting 2 or fewer heads out of the six is P X ≤ 2 = F(2) = , the cumulative value at x =2 in the righthand graph (which equals the sum of/ (n x)!x!)p x q nx n The number of trials x The number of successes p The probability of success q The probability of failure (which is 1 p) The binomial distribution describes the behavior of a count of variable X if the following conditions apply 1 The number of observations n is fixed 2 Each observation is



Tutorial Probability Distributions In Python Datacamp



The Binomial Distribution
Finding To calculate the probablity P(X x) by hand, we would have to calculate each individual probability, P(0), P(1), P(2), , P(x), and then add those together The TI/84 calculator has a built in function that does this calculation in one step The function is binomcdf (n, p, x) To calculate P(X 3) given n = 4, p = 041, and q = 059, press 2nd VARS DISTR, ARROW DOWN to select AThe Single Event Probability Calculator uses the following formulas P(E) = n(E) / n(T) = (number of outcomes in the event) / (total number of possible outcomes) P(E') = P(not E) = 1 P(E) Where P(E) is the probability that the event will occur, P(E') is the probability that the event will not occur, n(E) is the number of outcomes in the event E,Calculates a table of the probability mass function, or lower or upper cumulative distribution function of the Binomial distribution, and draws the chart
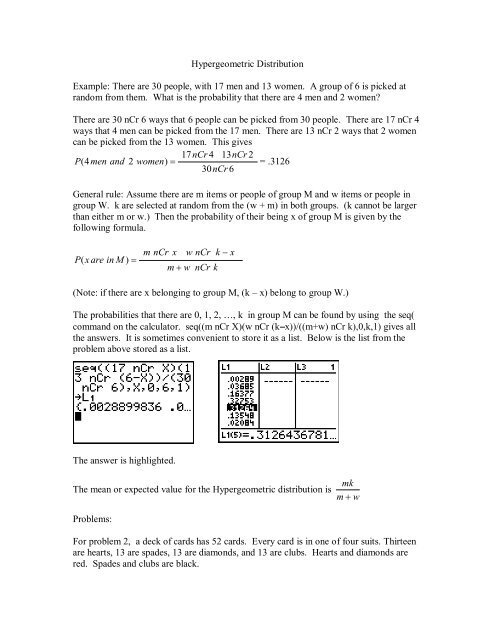


Hypergeometric Distribution And The Ti 84 Calculator


The Standard Normal Distribution
Binomial Probability Calculator This calculator will compute the probability of an individual binomial outcome (ie, a binomial probability), given the number of successes, the number of trials, and the probability of a successful outcome occurring Please enter the necessary parameter values, and then click 'Calculate'Negative Binomial Distribution Calculator This calculator is used to find the probability and cumulative probabilities for negative binomial random variable given the number of successes Read moreNegative Binomial Distribution Calculator with ExamplesProbability Formulas The Single Event Probability Calculator uses the following formulas P(E) = n(E) / n(T) = (number of outcomes in the event) / (total number of possible outcomes)



Normal Distribution Calculator High Accuracy Calculation


Http Condor Depaul Edu Ntomuro Courses It403 Notes Practiceproblems 5 2 Pdf
Poisson distribution calculator calculates the probability of given number of events that occurred in a fixed interval of time with respect to the known average rate of events occurred It's an online statistics and probability tool requires an average rate of success and Poisson random variable to find values of Poisson and cumulative Poisson distribution/ (n x)!x!)p x q nx n The number of trials x The number of successes p The probability of success q The probability of failure (which is 1 p) The binomial distribution describes the behavior of a count of variable X if the following conditions apply 1 The number of observations n is fixed 2 Each observation isUniform distribution probability (PDF) calculator, formulas & example work with steps to estimate the probability of maximim data distribution between the points a & b in statistical experiments By using this calculator, users may find the probability P(x), expected mean (μ), median and variance (σ 2) of uniform distributionThis uniform probability density function calculator is featured



Section 5 3 Binomial Probability Distributions Binomial Probability Distrtibution 1 The Procedure Has A Fixed Number Of Trials 2 The Trials Must Be Ppt Download
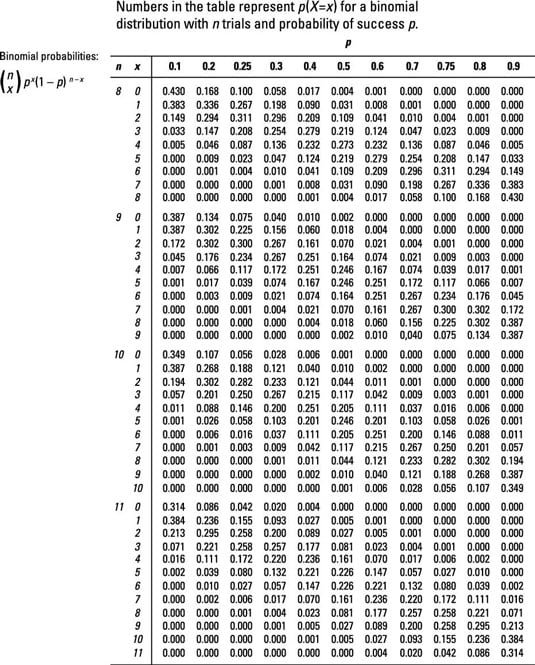


Figuring Binomial Probabilities Using The Binomial Table Dummies
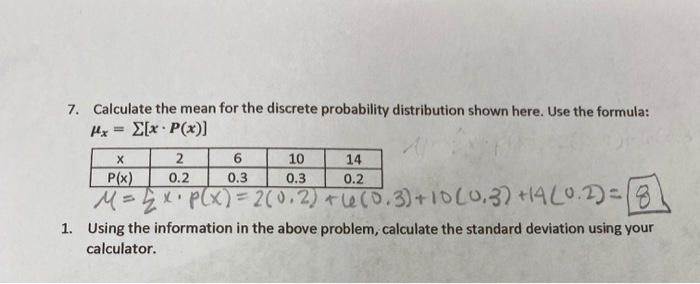


Solved 7 Calculate The Mean For The Discrete Probability Chegg Com



Solved Please Explain What You Did On The Calculator To G Chegg Com


Probability Calculator



Computing Binomial Probabilities Youtube


1



Probability With Discrete Random Variable Example Video Khan Academy


Q Tbn And9gcr25tef6v4nurws2kngeqzdif04iob3esypvergphtjedi 3mll Usqp Cau
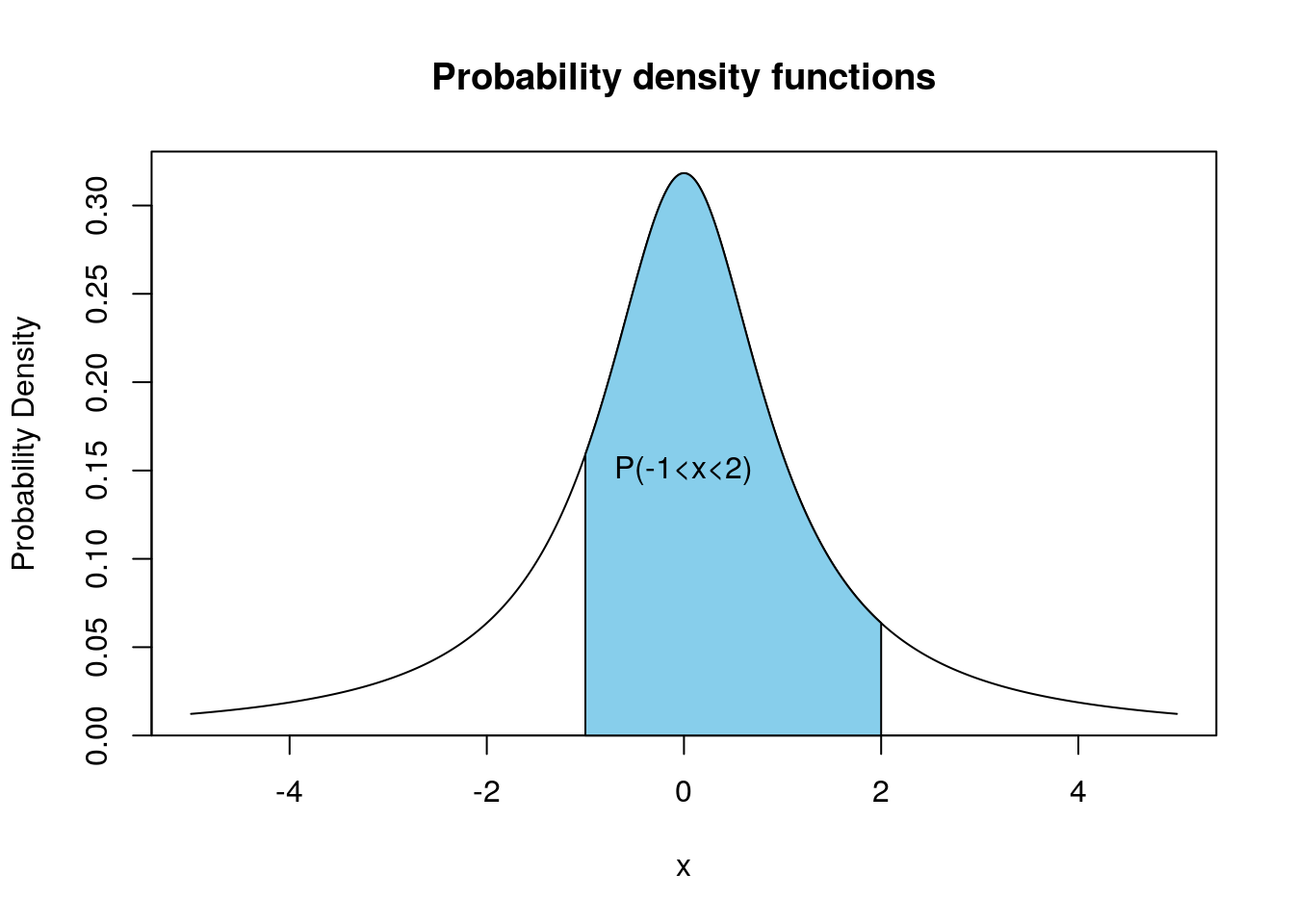


Chapter 8 Continuous Random Variables Introduction To Statistics And Data Science
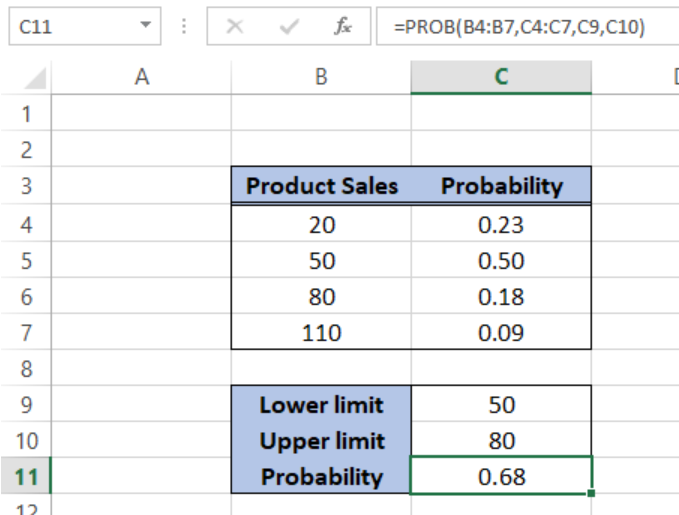


How To Calculate Probability In Excel Excelchat Excelchat



Solved 1 A Random Variable X Has The Probability Distr Chegg Com



Binomial Distribution Calculator With Step By Step Solution Vrcacademy
/JointProbabilityDefinition2-fb8b207be3164845b0d8706fe9c73b01.png)


Joint Probability Definition



4 Ways To Calculate Probability Wikihow
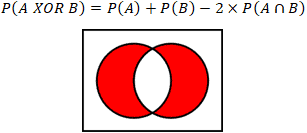


Probability Calculator
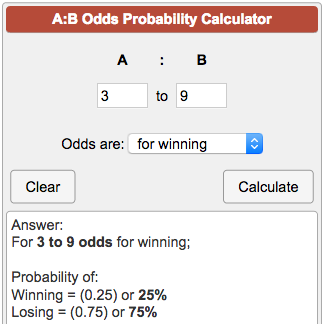


Odds Probability Calculator



How To Quickly Find Probabilities Using Binomial Pd And List Casio Classwiz Fx 991ex Fx 570exthe Calculator Guide Calculator Probability Graphing Calculator


2


Www Coconino Edu Resources Files Pdfs Academics Sabbatical Reports Kate Kozak Chapter 5 Pdf
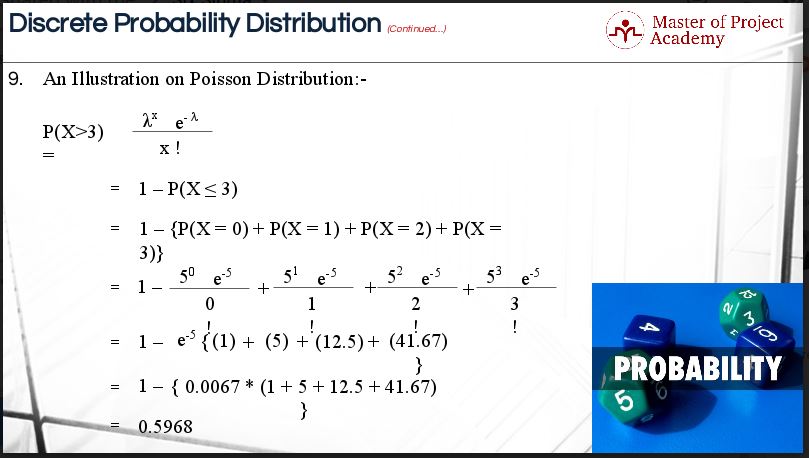


How To Calculate Probability Using The Poisson Distribution


1



Calculating Binomial Probabilities On The Ti 84 Probability Lessons Probability Graphing



Random Variable Probability Distribution P X Greater Than X 3p X Less Than 2 Ib Math Youtube


Binomial Random Variables Biostatistics College Of Public Health And Health Professions University Of Florida



Pdf Normdis Free Two Way Calculator For The Normal Probability Distribution And The Z Test With Graphics
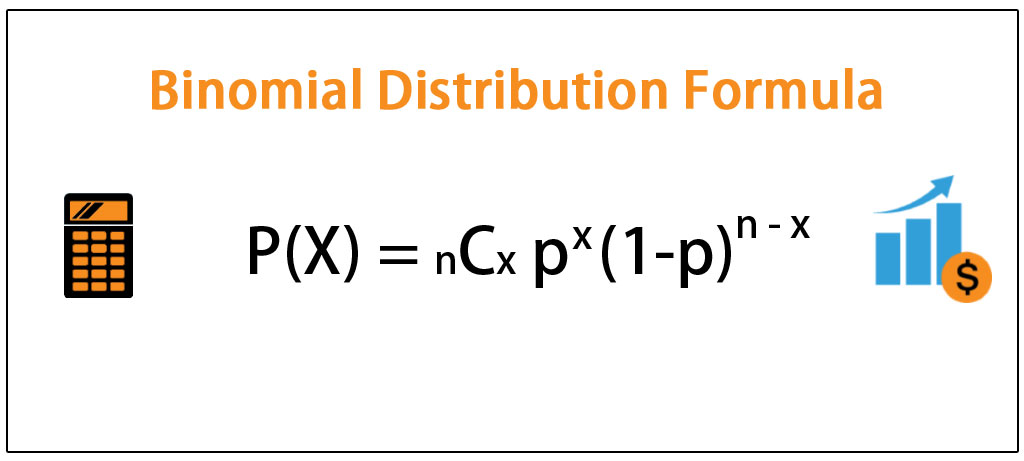


Binomial Distribution Formula Step By Step Calculation Example
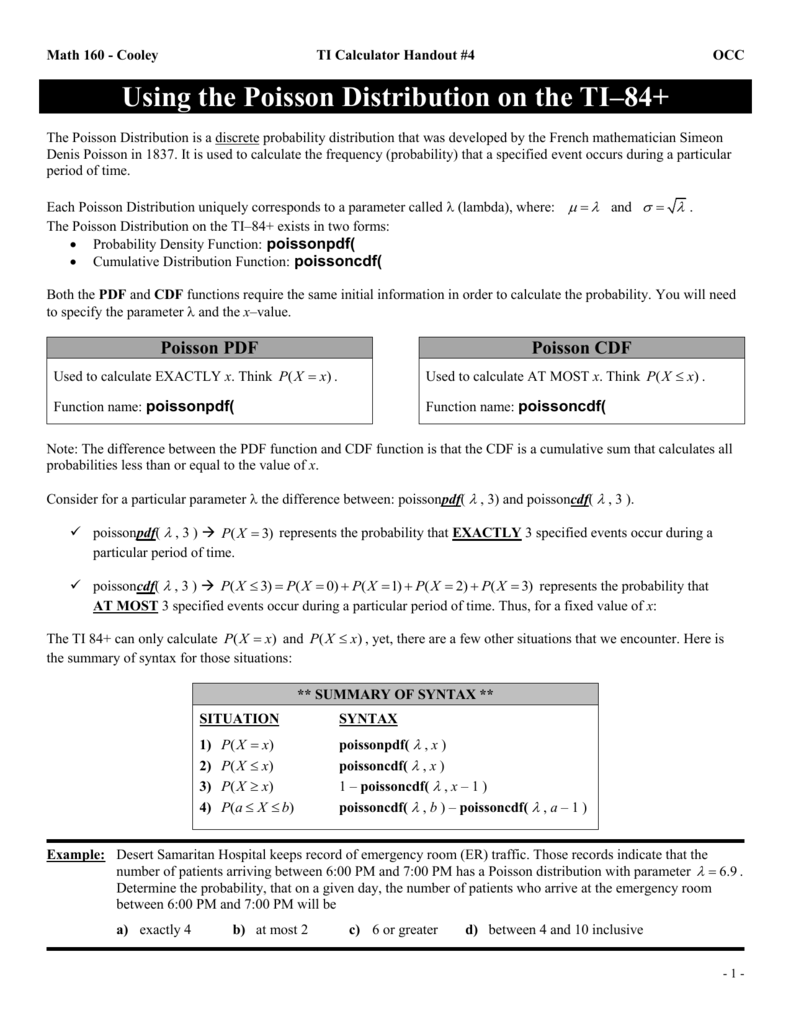


Math 160 Ti Calculator Handout 4
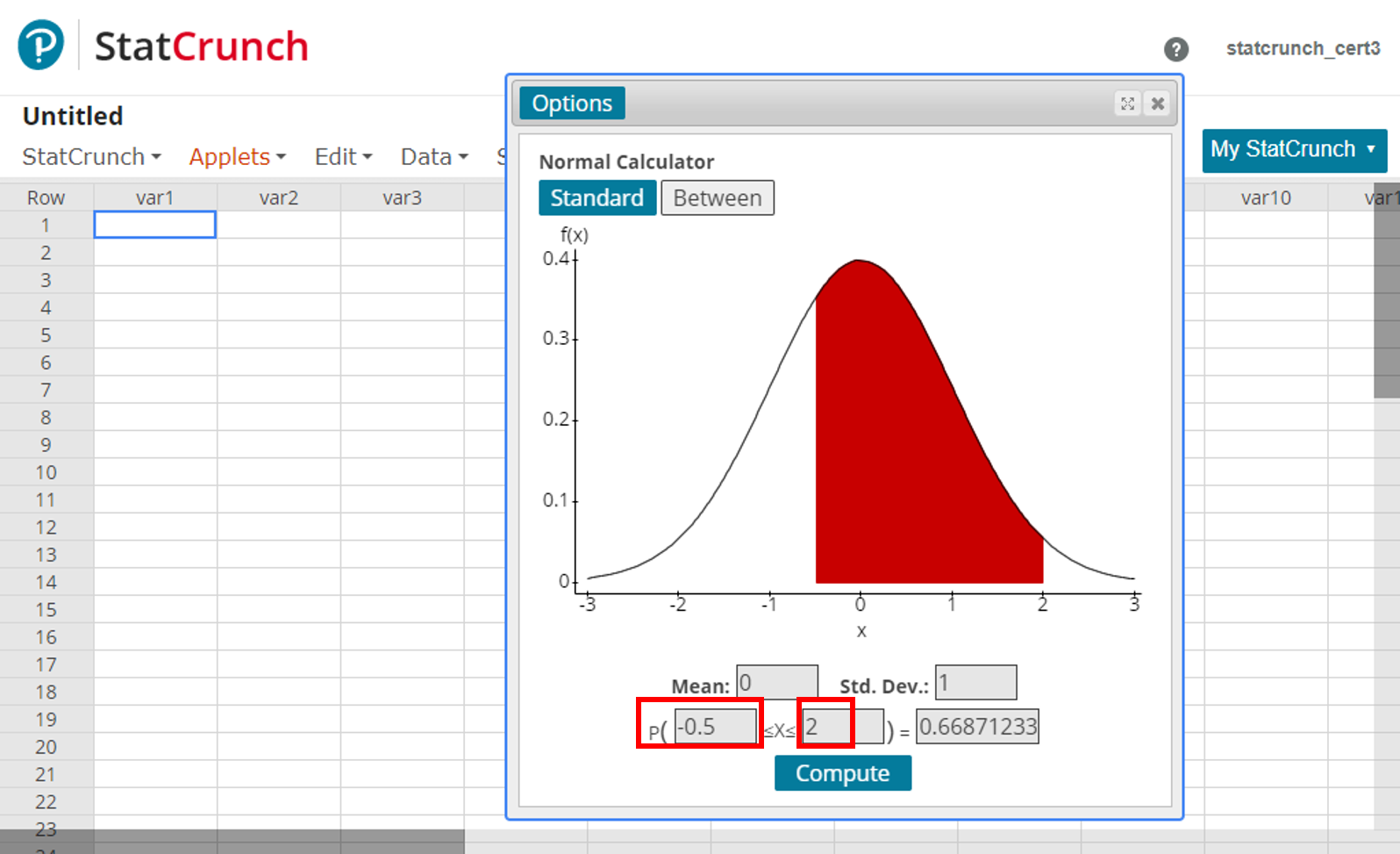


Graphical Calculators For Continuous Distributions



Mean Expected Value Of A Discrete Random Variable Video Khan Academy
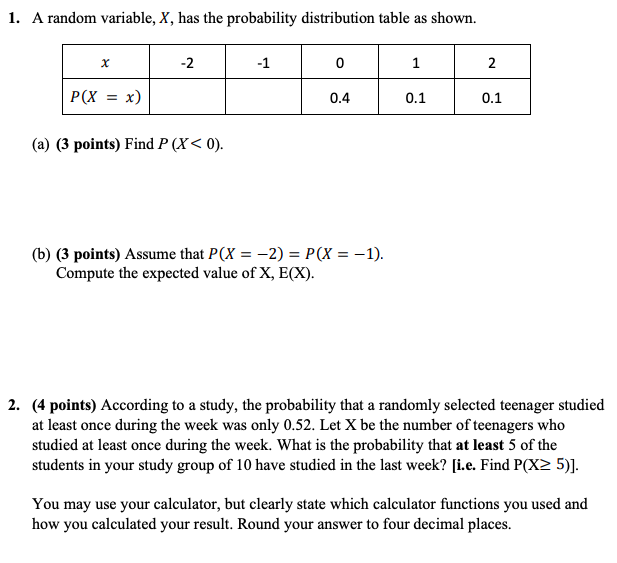


Solved 1 A Random Variable X Has The Probability Distr Chegg Com



Binomial Probability Example Video Khan Academy
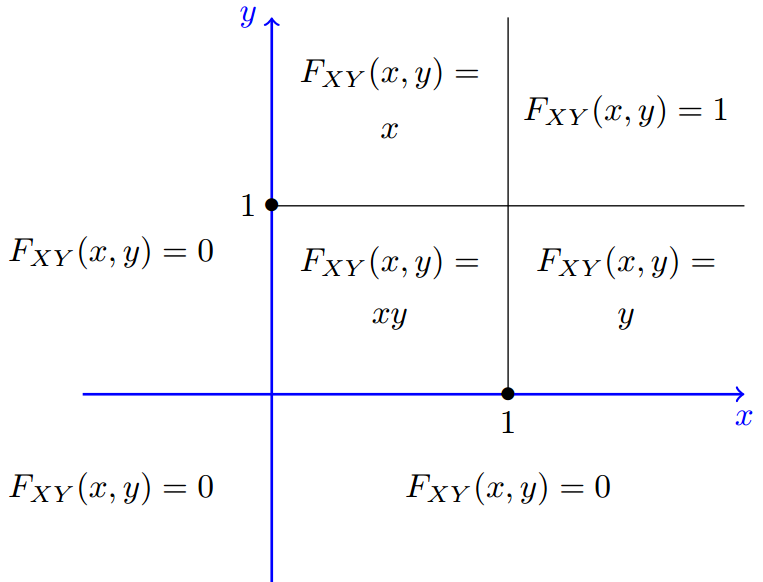


Joint Cumulative Distribution Function Examples Cdf
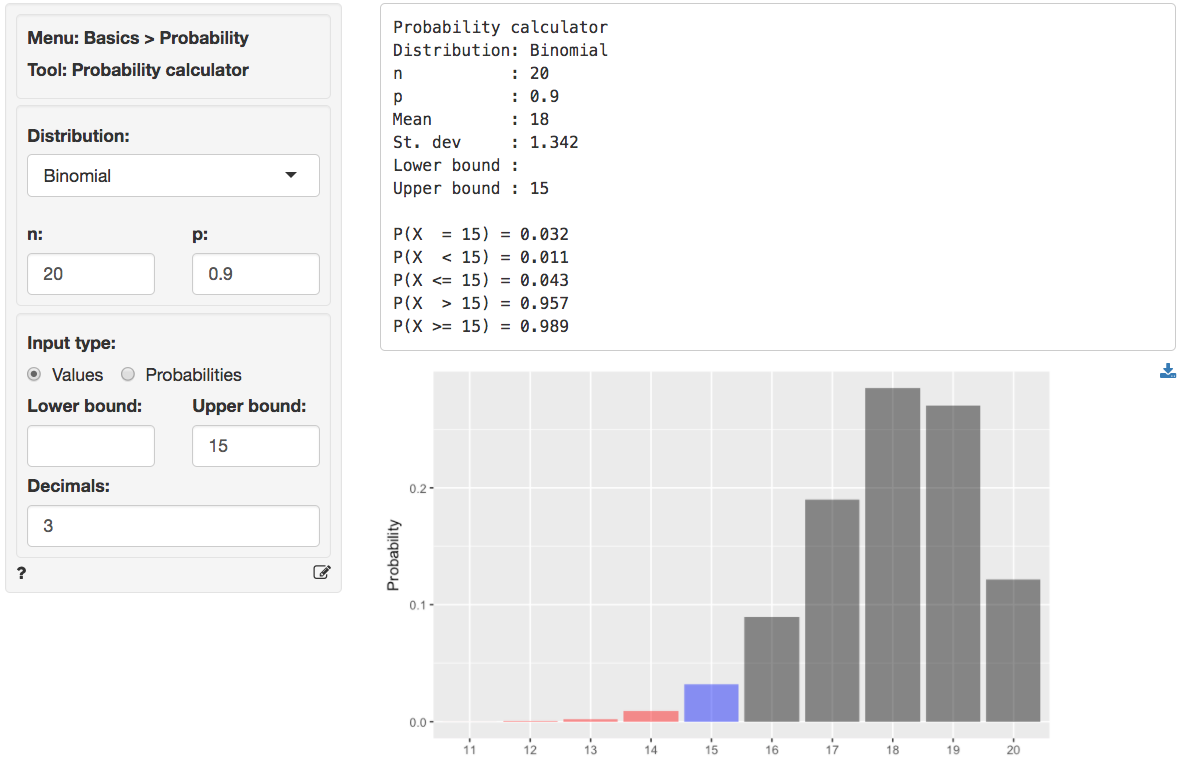


Basics Probability Probability Calculator


Www Utdallas Edu Efrom Solhw Pdf
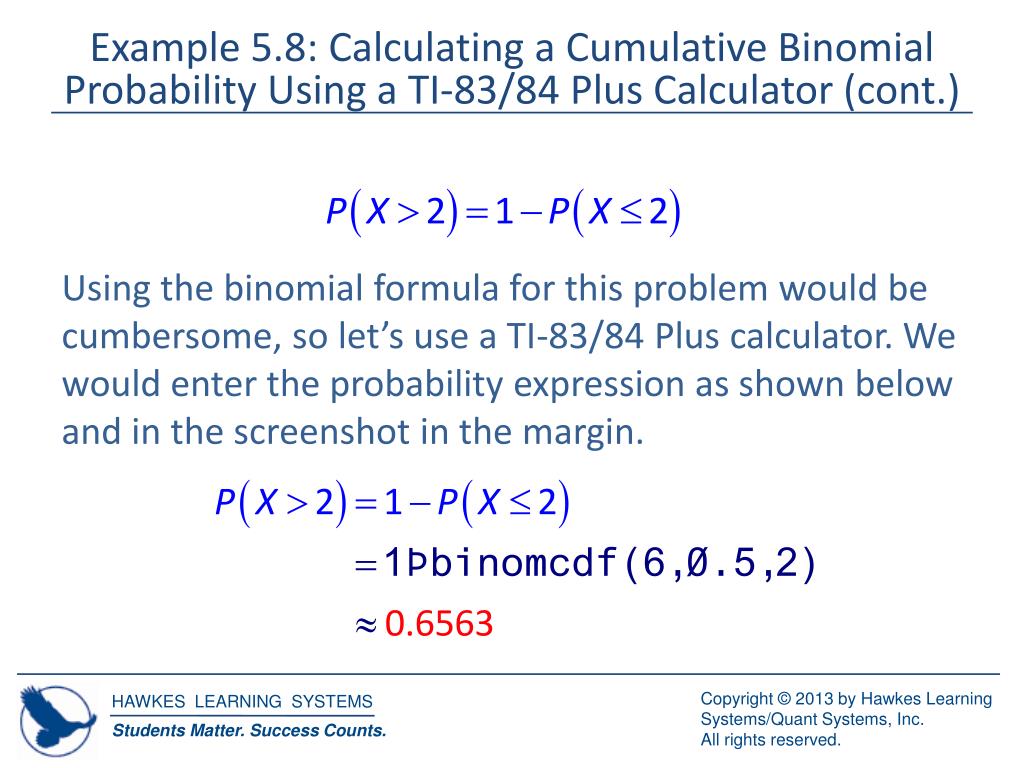


Ppt Section 5 2 Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id



Random Variable And Its Probability Distribution Ma Economics Karachi University


Standard Normal Distribution Biostatistics College Of Public Health And Health Professions University Of Florida
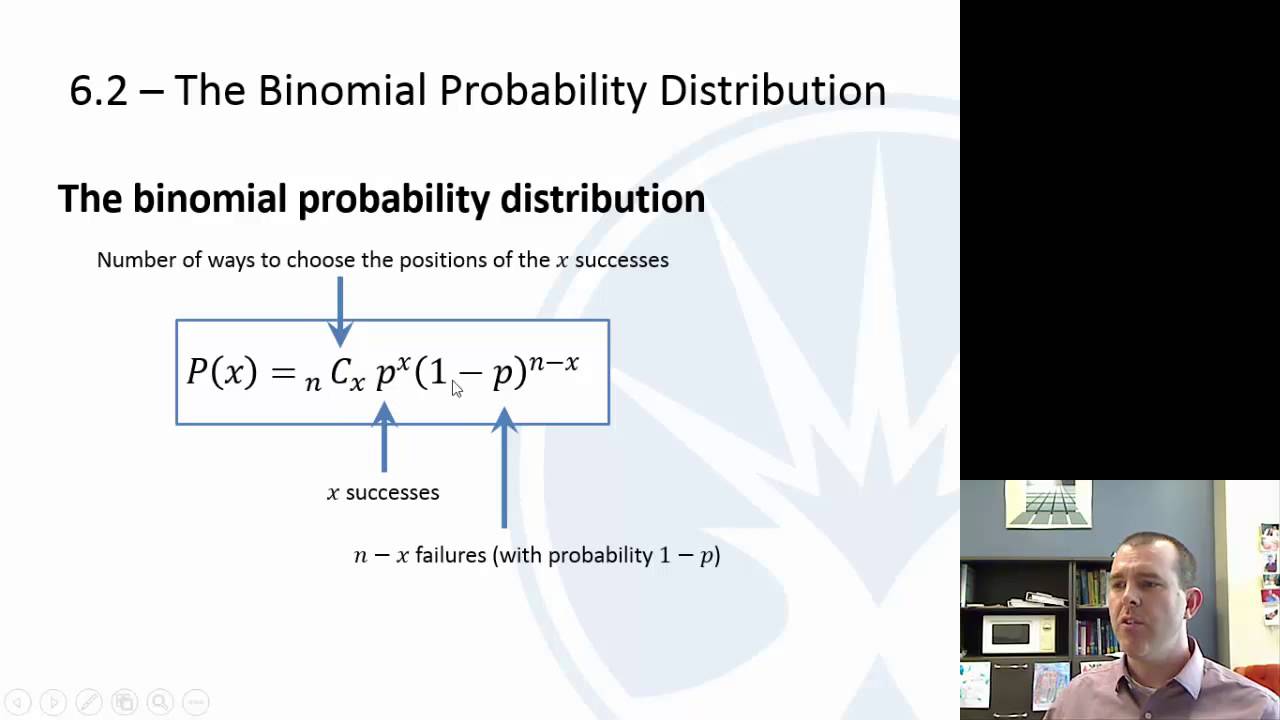


Chapter 6
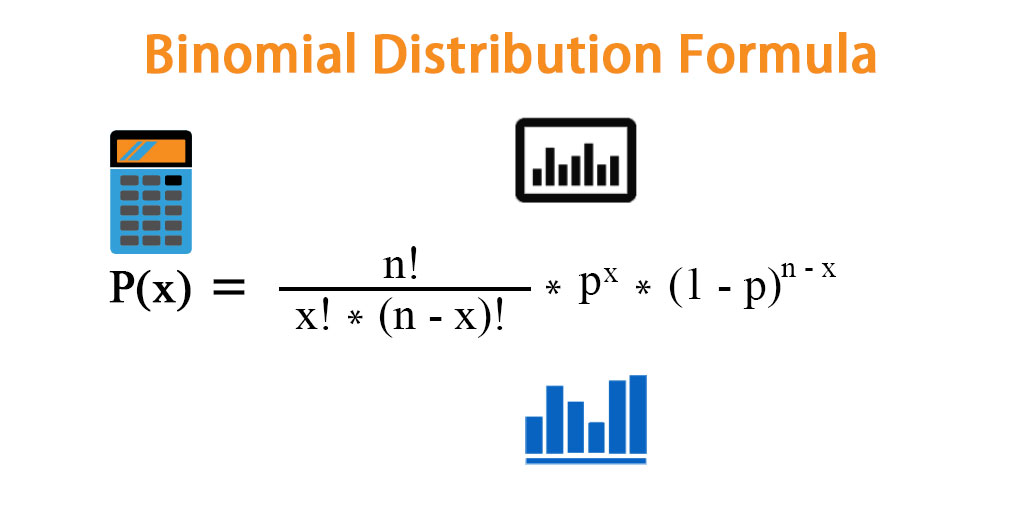


Binomial Distribution Formula Calculator Excel Template


Q Tbn And9gctqsop5xoyrsdnd92znktpup9 Ctr1ohag3khqngrp Ali2fxrt Usqp Cau
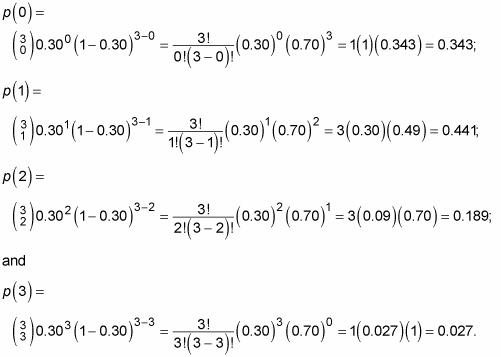


How To Find Binomial Probabilities Using A Statistical Formula Dummies



Binomial Distribution Calculator



Binomial Distribution Calculator High Accuracy Calculation


Http Faculty Tcu Edu Gfriedman Stats Calculators Pdf
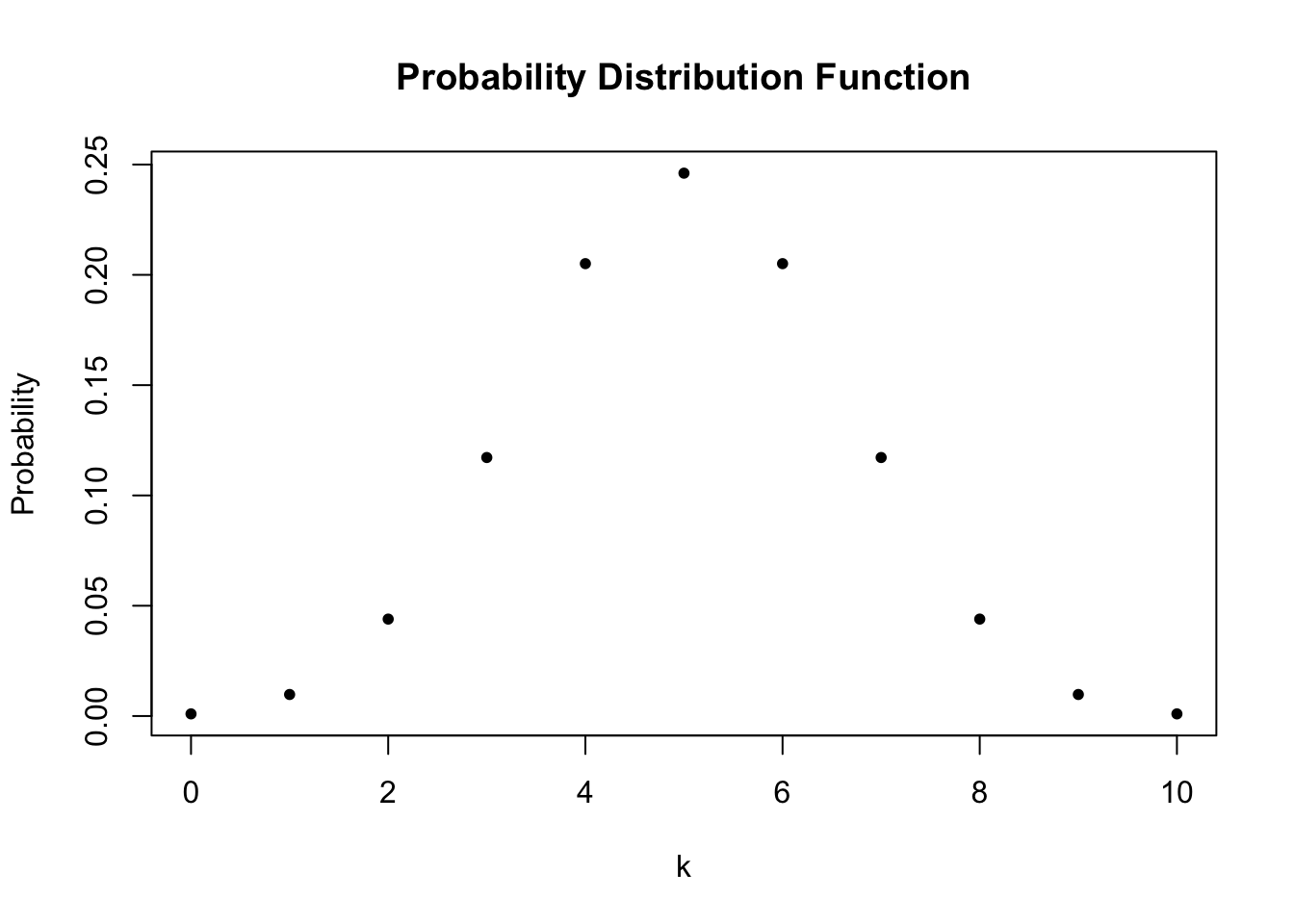


2 1 Random Variables And Probability Distributions Introduction To Econometrics With R


Binomial Distribution Workout For N 18 P 0 36 X 12



Content Mean And Variance Of A Continuous Random Variable
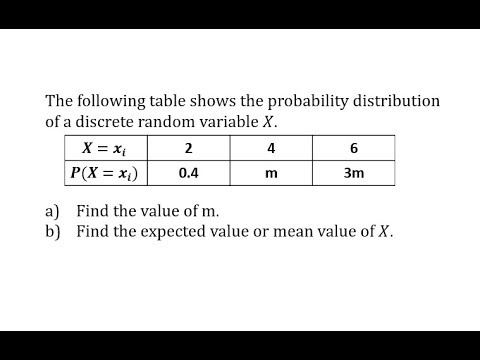


Find Probabilities And Expected Value Of A Discrete Probability Distribution Youtube



Binomial Probabilities Examples Calculator Mathbootcamps
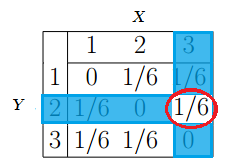


Joint Probability And Joint Distributions Definition Examples Statistics How To



Binomial Distribution Calculator
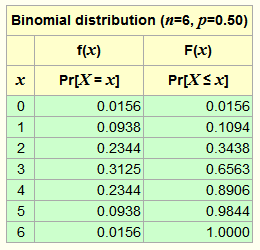


Binomial Distribution Calculator
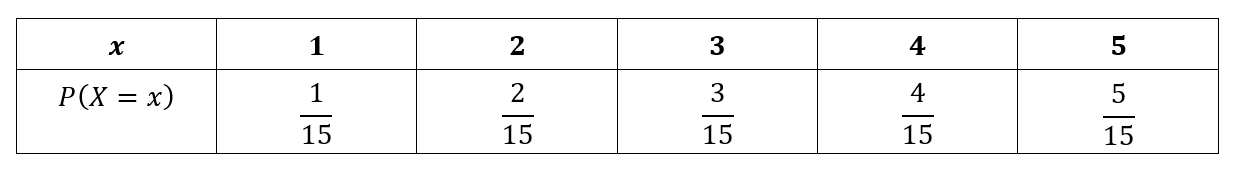


Discrete Random Variables Probability Distribution Functions
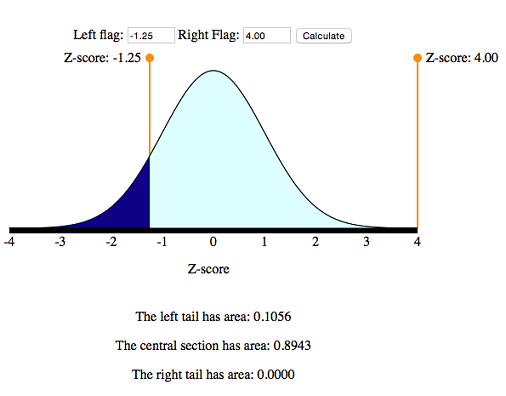


Normal Random Variables 6 Of 6 Concepts In Statistics



Probability Distribution Formula Examples With Excel Template
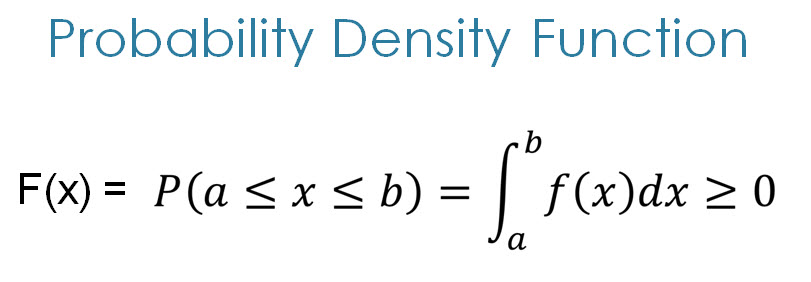


Continuous Probability Distributions Env710 Statistics Review Website


Binomial Probability Calculator With A Step By Step Solution Statistics Helper



Dice Probability Calculator



Radiant Tutorial Series Probability Calculator Video 1 Youtube
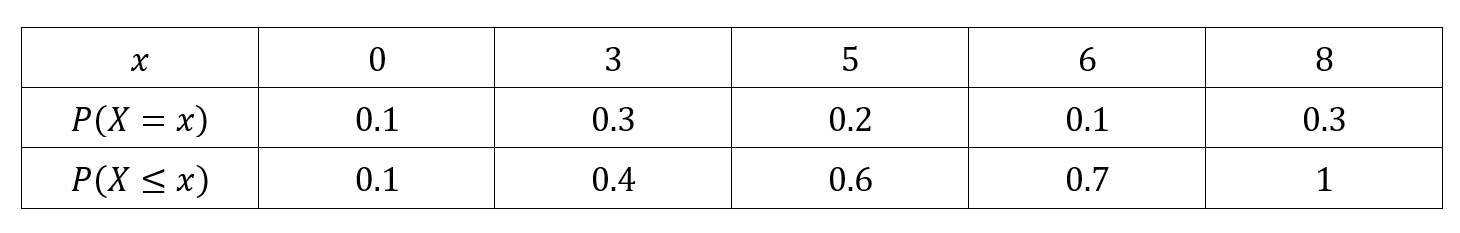


Parameters Of Discrete Random Variables



Binomial Distribution Calculator Binomial Probability Calculator Binomial Cdf Calculations



Binomial Distribution Calculator
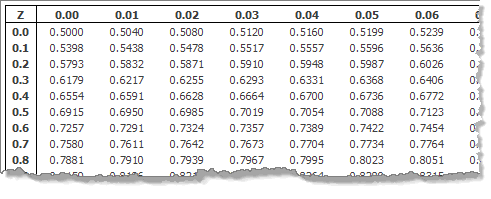


How To Do Normal Distributions Calculations Laerd Statistics



Graphical Calculators For Continuous Distributions



6 2 Using The Normal Distribution Texas Gateway
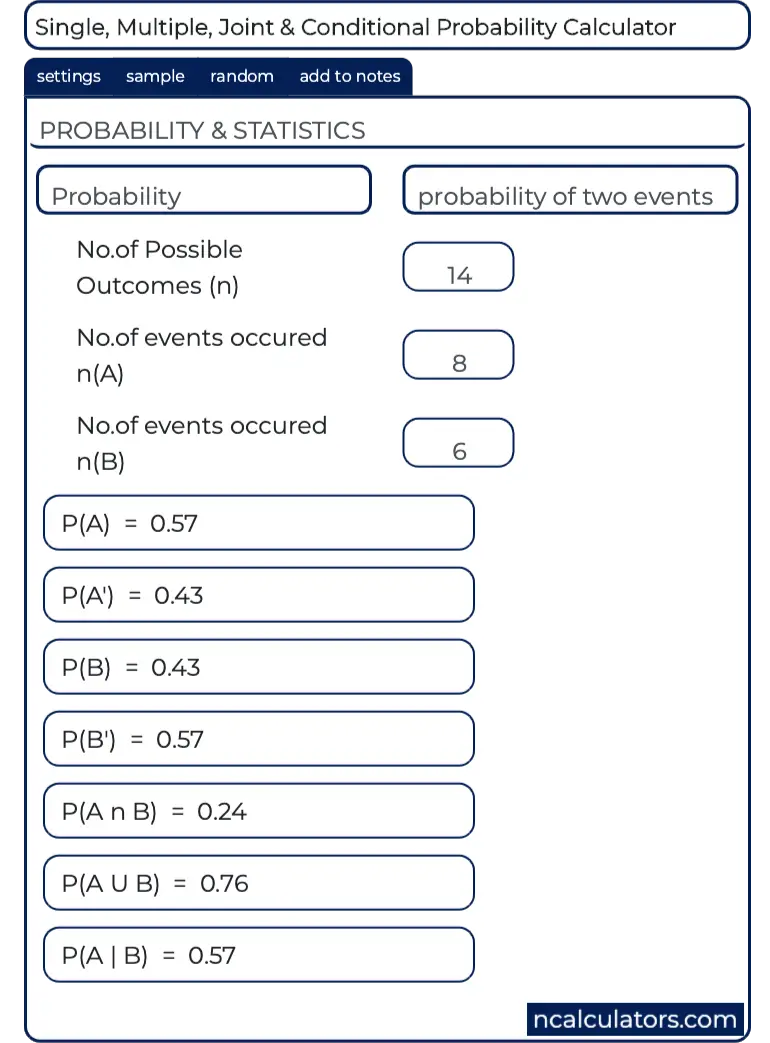


Probability Calculator



Probability Calculator


Binomial Formula Explained


Integral


Probability Density Function



4 1 Probability And Discrete Probability Distributions



Pdf T Tester Free Two Way Calculator For Student S T Test With Graphics



Negative Binomial Distribution Calculator Vrcacademy


Www3 Nd Edu Dgalvin1 101 101 S16 Topic 8p7 Galvin Pdf
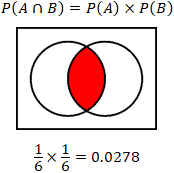


Probability Calculator
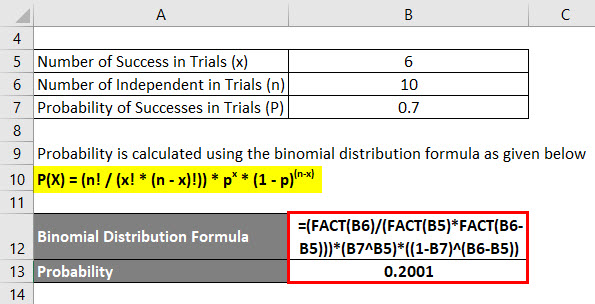


Binomial Distribution Formula Calculator Excel Template


Section 4 Bivariate Distributions


コメント
コメントを投稿